








| Extension | Source Type |
|---|---|
| .h | Header files. Header files contain class, type, function, and constant declarations. |
| .m | Source files. This is the typical extension used for source files and can contain both Objective-C and C code. |
| .mm | Source files. A source file with this extension can contain C++ code in addition to Objective-C and C code. This extension should be used only if you actually refer to C++ classes or features from your Objective-C code. |
@interface MyClass : NSObject
{
int count;
id data;
NSString* name;
}
- (id)initWithString:(NSString*)aName;
+ (MyClass*)createMyClassWithString:(NSString*)aName //Class method;
@end@implementation MyClass
- (id)initWithString:(NSString *)aName
{
self = [super init];
if (self) {
name = [aName copy];
}
return self;
}
+ (MyClass *)createMyClassWithString: (NSString *)aName
{
return [[self alloc] initWithString:aName] ;
}
@end//create an Object of SomeClass:
id anObject = [[SomeClass alloc] init];
//Example init method implementation in NSObject:
- (id)init {
self = [super init];
if (self) {
//initialisation of Object
}
return self;
}NSString* text1 = [[NSString alloc] initWithCString: "Hello World!" encoding: NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSString* text2 = @"Hello World!"; //short for upper statement
NSLog(@"text 1 = %@", text1); //%@ placeholder for objects
NSLog(@"text 2 = %@", text2);
NSLog(@"text2.length = %ld", text2.length);
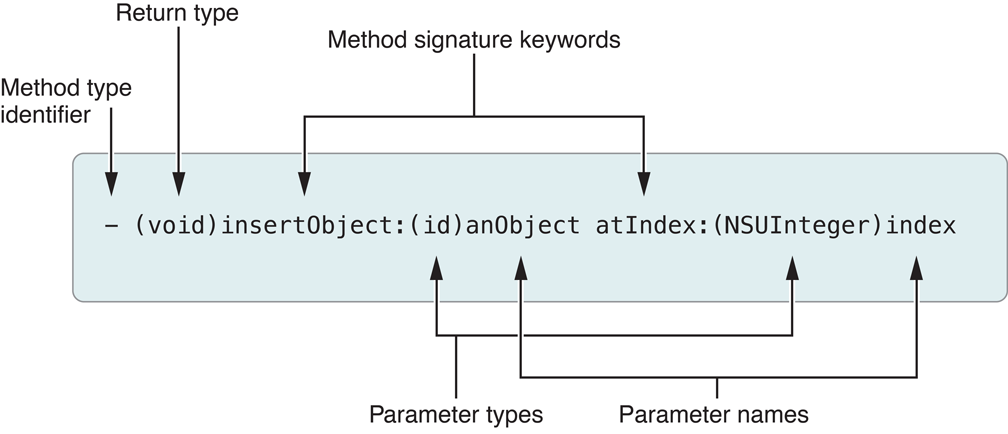
[myArray insertObject:anObject atIndex:0];[[myAppObject theArray] insertObject: [myAppObject objectToInsert] atIndex: 0];// message without argument
[receiver message];
// message with single argument
[receiver message: argument];
// message with multiple arguments
[receiver message: arg1 argument2: arg2];
// receiving a return value
int status = [receiver message];
// message with a variable number of arguments
[receiver makeGroup: group, memberOne, memberTwo, memberThree];
// nil is essentially the same as NULL
NSMutableArray *myArray = nil;
// Create a new array and assign it to the myArray variable.
myArray = [NSMutableArray array];
Person* myPerson; // Strong typing
id myObject; // Weak typing//Dynamic binding example
@interface ClassA : NSObject {…}
- (void) doSomething;
@end
@interface ClassB : NSObject { …}
- (void) doSomething;
@end
// anywhere
id object = … // An object of an arbitrary class
[object doSomething]; // polymorph between ClassA und ClassBPlease open the terminal and create your first Objective-C project.
Objective-C:
NSString *helloWorld = @"Hello World";
NSLog(@"%@", helloWorld);Swift:
var str = "Hello World"
print(str)